Residential Schools
Synopsis:
In May 2021, the world was shocked by news of the detection of 215 unmarked graves on the grounds of the former Kamloops Indian Residential School (KIRS) in British Columbia, Canada. Ground-penetrating radar confirmed the deaths of students as young as three in the infamous residential school system, which systematically removed children from their families and brought them to the schools. At these Christian-run, government-supported institutions, they were subjected to physical, mental, and sexual abuse while their Indigenous languages and traditions were stifled and denounced. The egregious abuses suffered in residential schools across the continent caused - as the 2021 discoveries confirmed - death for too many and a multigenerational legacy of trauma for those who survived.
"Tsquelmucwilc" (pronounced cha-CAL-mux-weel) is a Secwepemc phrase loosely translated as "We return to being human again." Tsqelmucwilc is the story of those who survived the Kamloops Indian Residential School, based on the 1988 book Resistance and Renewal, a groundbreaking history of the school - and the first book on residential schools ever published in Canada. Tsqelmucwilc includes the original text as well as new material by the original book's author, Celia Haig-Brown; essays by Secwepemc poet and KIRS survivor Garry Gottfriedson and Nuu-chah-nulth elder and residential school survivor Randy Fred; and first-hand reminiscences by other survivors of KIRS, as well as their children, on their experience and the impact of their trauma throughout their lives.
Read both within and outside the context of the grim 2021 discoveries, Tsqelmucwilc is a tragic story in the history of Indigenous peoples of the indignities suffered at the hands of their colonizers, but it is equally a remarkable tale of Indigenous survival, resilience, and courage.
Additional Information
240 pages | 6.00" x 8.00" | B&W photos throughout | Paperback
Synopsis:
The Assiniboia school is unique within Canada’s Indian Residential School system. It was the first residential high school in Manitoba and one of the only residential schools in Canada to be located in a large urban setting. Operating between 1958 and 1973 in a period when the residential school system was in decline, it produced several future leaders, artists, educators, knowledge keepers, and other notable figures. It was in many ways an experiment within the broader destructive framework of Canadian residential schools.
Stitching together memories of arrival at, day-to-day life within, and departure from the school with a socio-historical reconstruction of the school and its position in both Winnipeg and the larger residential school system, Did You See Us? offers a glimpse of Assiniboia that is not available in the archival records. It connects readers with a specific residential school and illustrates that residential schools were often complex spaces where forced assimilation and Indigenous resilience co-existed.
These recollections of Assiniboia at times diverge, but together exhibit Survivor resilience and the strength of the relationships that bond them to this day. The volume captures the troubled history of residential schools. At the same time, it invites the reader to join in a reunion of sorts, entered into through memories and images of students, staff, and neighbours. It is a gathering of diverse knowledges juxtaposed to communicate the complexity of the residential school experience.
Reviews
“Remembering Assiniboia is a thoughtful, community based project rooted in the needs of the Assiniboia Residential School community. This book is a must read for those working on the history of Residential Schools and those engaged in community based restorative justice projects.” — Krista McCracken
"Did You See Us? was born out of a reunion, and readers are invited to the reverberations of this coming together. It offers multi-vocal perspectives primarily from survivors but also from non-Indigenous staff, archival documents, and settler community members. As the Truth and Reconciliation Commission begins to accumulate anniversaries, now more than ever the testimonies of residential school survivors are much needed." — Jane Griffith
Educator Information
Table of Contents
Dedication
Land Acknowledgement Statement/ Theodore Fontaine
Preface / Theodore Fontaine
Section One: The Residential Years (1958-1967)
Section Two: The Hostel Years (1967-1973)
Section Three: Assiniboia and the Archives
Section Four: Staff Remembrances
Section Five: Neighbours
Section Six: Winnipeg Remembers
Section Seven: Reunion and Remembrance
Additional Information
272 pages | 6.00" x 8.50" | bibliography
Synopsis:
One of the few accounts by care-givers in an Indian Residential School describing the horrific conditions.
In 1970, the authors, Nancy Dyson and Dan Rubenstein, were hired as childcare workers at the Alert Bay Student Residence (formerly St. Michael's Indian Residential School) on northern Vancouver Island. Shocked when Indigenous children were forcibly taken from their families, punished for speaking their native language, fed substandard food and severely disciplined for minor offences, Dan and Nancy questioned the way the school was run with its underlying missionary philosophy. When a delegation from the Department of Indian and Northern Affairs visited St. Michael's, the couple presented a long list of concerns, which were ignored. The next day they were dismissed by the administrator of the school. Some years later, in 2015, the Truth and Reconciliation Commission Reports were released. The raw grief and anger of residential school survivors were palpable and the authors' troubling memories of St. Michael's resurfaced. Dan called Reconciliation Canada, and Chief Dr. Robert Joseph encouraged the couple to share their story with today's Canadians.
St. Michael's Residential School: Lament and Legacy is a moving narrative - one of the few told by caregivers who experienced on a daily basis the degradation of Indigenous children. Their account will help to ensure that what went on in the Residential Schools is neither forgotten nor denied.
Additional Information
200 pages | 6.00" x 9.00"
Synopsis:
Young Dominique Rankin was intended to succeed his father as Algonquin Hereditary Chief and Medicine Man. Before that could happen, the Government of Canada’s policies of Indigenous assimilation wrested the boy from his home to entrust him to the infamous Indian residential school system. There, like thousands of Indigenous children across North America, Dominique would endure a terrible ordeal. Only upon leaving the school years later would the young man finally be free to begin a long journey of healing and self-discovery that would reunite him with his heritage and his true destiny.
Weaving the Prophecy of the Seven Fires’ teachings with the powerful narrative of his own tumultuous life, Chief Dominique Rankin delivers a vibrant testimony on respect, forgiveness, and healing. In this poignant memoir, the residential school Survivor, Elder, Medicine Man, and former Grand Chief of the Algonquin Nation bares all—the dark and the light alike—to unshroud a chapter of our sombre collective past and to illuminate a path to a better, brighter future.
Additional Information
160 pages | 6.00" x 9.00" | Paperback
Synopsis:
In this poetic, poignant memoir, Dene artist and social activist Antoine Mountain paints an unforgettable picture of his journey from residential school to art school—and his path to healing.
In 1949, Antoine Mountain was born on the land near Radelie Koe, Fort Good Hope, Northwest Territories. At the tender age of seven, he was stolen away from his home and sent to a residential school—run by the Roman Catholic Church in collusion with the Government of Canada—three hundred kilometres away. Over the next twelve years, the three residential schools Mountain was forced to attend systematically worked to erase his language and culture, the very roots of his identity.
While reconnecting to that which had been taken from him, he had a disturbing and painful revelation of the bitter depths of colonialism and its legacy of cultural genocide. Canada has its own holocaust, Mountain argues.
As a celebrated artist and social activist today, Mountain shares this moving, personal story of healing and the reclamation of his Dene identity.
Educator Information
Recommended in the Canadian Indigenous Books for Schools 2019-2020 resource list as being useful for grades 9 to 12 in the following subject areas: English Language Arts, Social Studies.
Included in this story are personal stories of residential school and addiction.
Additional Information
272 pages | 5.50" x 8.50"
Synopsis:
Quebec author An Antane Kapesh's two books, Je suis une maudite sauvagesse (1976) and Qu'as-tu fait de mon pays? (1979), are among the foregrounding works by Indigenous women in Canada. This English translation of these works, presented alongside the revised Innu text, makes them available for the first time to a broader readership.
In I Am a Damn Savage, Antane Kapesh wrote to preserve and share her culture, experience, and knowledge, all of which, she felt, were disappearing at an alarming rate because many Elders – like herself – were aged or dying. She wanted to publicly denounce the conditions in which she and the Innu were made to live, and to address the changes she was witnessing due to land dispossession and loss of hunting territory, police brutality, and the effects of the residential school system. What Have You Done to My Country? is a fictional account by a young boy of the arrival of les Polichinelles and their subsequent assault on the land and on native language and culture.
Through these stories Antane Kapesh asserts that settler society will eventually have to take responsibility and recognize its faults, and accept that the Innu – as well as all the other nations – are not going anywhere, that they are not a problem settlers can make disappear.
Additional Information
216 pages | 5.25" x 8.00" | Translation and Afterword by Sarah Henzi
Synopsis:
Andy and Phyllis Chelsea met during their years spent at the St. Joseph’s Mission School in Williams Lake, BC. Like the thousands of others forced into the church-run residential school system, Andy and Phyllis are no strangers to the ongoing difficulties experienced by most Indigenous peoples in Canada. The couple married in 1964 but brought the trauma of their mission school years into their marriage. The Chelseas’ struggle with alcohol came to an abrupt halt in 1971 when their daughter, Ivy, then aged seven, stated that she and her brothers did not want to live with their parents because of the drinking, that they would stay with their Grandmother, their Kye7e. Andy and Phyllis chose sobriety to preserve their family. This decision sparked a lifetime of activism for the couple, which included overcoming the challenges caused by Canada’s disregard for their community. Throughout the twenty-seven years Andy was Chief of the Alkali Lake Esk’et First Nation, the Chelseas worked to eradicate alcoholism and took steps to overcome the rampant intergenerational trauma that existed for the people of Alkali Lake. Their efforts, their story and the perseverance of the members of their village have inspired Indigenous groups facing similar struggles throughout the world.
Resolve: The Chelsea Story and a First Nation Community’s Will to Heal explores the harrowing, personal journey of the Chelseas. By combining personal interviews and historical records, biographer Carolyn Parks Mintz shares the Chelseas’ transition from residential schools to state-sanctioned reservations to international recognition of their activism in the face of ongoing repression. A simultaneous celebration of strength and a condemnation of systemic racism, Resolve is a personal and deeply moving story that calls for a closer look at the status of Canada’s reconciliation efforts from the Chelseas’ perspective.
Educator Information
Recommended in the Canadian Indigenous Books for Schools 2020/2021 resource list for grades 10 to 12 for English Language Arts, Social Studies, and Social Justice.
Caution: Alcoholisms, trauma, physical and sexual abuse.
Additional Information
240 pages | 6.00" x 9.00"
Synopsis:
Indigenous perspectives much older than the nation itself shared through maps, artwork, history and culture.
The Royal Canadian Geographical Society, in partnership with Canada's national Indigenous organizations, has created a groundbreaking four-volume atlas that shares the experiences, perspectives, and histories of First Nations, Inuit and Métis peoples. It's an ambitious and unprecedented project inspired by the Truth and Reconciliation Commission's Calls to Action. Exploring themes of language, demographics, economy, environment and culture, with in-depth coverage of treaties and residential schools, these are stories of Canada's Indigenous Peoples, told in detailed maps and rich narratives.
This extraordinary project offers Canada a step on the path toward understanding.
The volumes contain more than 48 pages of reference maps, content from more than 50 Indigenous writers; hundreds of historical and contemporary photographs and a glossary of Indigenous terms, timelines, map of Indigenous languages, and frequently asked questions. All packaged together in a beautifully designed protective slipcase.
Educator Information
Recommended for ages 13+.
The Indigenous Peoples Atlas of Canada includes a four volume print atlas, an online atlas, an app, and more!
Additional Information
322 pages | 10.50" x 12.87"
Synopsis:
This groundbreaking anthology from territory that is now Saskatchewan, kisiskâciwan, includes rich oral narratives from Cree, Saulteaux, Nakoda, Dakota, Dene, and Métis cultures; early writings from Cree missionaries; speeches and letters by Treaty Chiefs; stories from elders; archival discoveries; and contemporary literary works in all genres.
Historically and culturally comprehensive, voices include Big Bear, Thunderchild, Louis Riel, Gabriel Dumont, Edward Ahenakew, Maria Campbell, Buffy Sainte-Marie, Rita Bouvier, Harold Johnson, Gregory Scofield, Warren Cariou, Louise Halfe, and many more.
Educator Information
The collected works in this anthology would be useful for high school and college/university courses. All the works in this anthology are connected to Saskatchewan in some way. Some themes include Residential Schools, family, resilience, the Sixties Scoop, and coming of age.
Recommended resource for Grades 10-12 for these subjects: Drama, English Language Arts, Social Studies.
Caution: Some of the works in this anthology contain mature subject matter, such as discussion of abuse, violence, sexuality, etc.
Additional Information
300 pages | 6.00" x 9.00"
Authenticity Note: This work is labelled as containing Authentic Indigenous Text because of the contributions from Indigenous Peoples.
Synopsis:
Speaking Our Truth: A Journey of Reconciliation is a nonfiction book for middle readers that examines how we can foster Reconciliation in an accessible way. Centered around the writings of Monique Gray Smith, this teacher guide is a comprehensive support for educators focusing on Indigenous teachings and looking to build an inquiry-based unit plan about Reconciliation. Activities such as essential questions from the author, metaphors for learning and cross-curricular plans are laid out clearly, with instructions and appropriate vocabulary for teachers and students to embark on this journey of Reconciliation together.
Educator Information
This resource helps teachers embark on a journey of Reconciliation in the classroom. The author, Tasha Henry, holds a Master of Education in Language, Culture and Teaching from York University and has been teaching for over twenty years.
Recommended in the Canadian Indigenous Books for Schools 2019-2020 resource list as being a useful Teacher Resource with regard to English Language Arts, Social Justice, and Social Studies.
Find the student resource here: Speaking Our Truth: A Journey of Reconciliation
Additional Information
46 pages | 8.50" x 11.00"
Synopsis:
Power through Testimony documents how survivors are remembering and reframing our understanding of residential schools in the wake of the 2007 Indian Residential Schools Settlement Agreement and the Truth and Reconciliation Commission (TRC), a forum for survivors, families, and communities to share their memories and stories with the Canadian public. The commission closed and reported in 2015, and this timely volume reveals what happened on the ground.
Drawing on field research during the commission and in local communities, the contributors reveal how survivors are unsettling colonial narratives about residential schools and how the churches and former school staff are receiving or resisting the “new” residential school story. Part 1 details how residential schools have been understood and represented by various groups and individuals over time and how survivors’ testimonies at the commission are changing those representations. Part 2 examines whether the stories of abuse and trauma now circulating are overpowering less sensational stories, preventing other voices and memories from surfacing in local communities. Part 3 explores how the churches and former school staff have received this new testimony and what their response means for future relations with Aboriginal peoples across the country.
Power through Testimony shows that by bringing to light new stories about residential schools and by encouraging the denunciation of other historical wrongs, the TRC was more than a symbolic act. Ultimately, however, the contributors question the power of the TRC to unsettle dominant colonial narratives about residential schools and transform the relationship between Indigenous people and Canadian society.
As one of the first books published on Canada’s Truth and Reconciliation Commission, Power through Testimony will be of interest to students and scholars of Aboriginal studies, anthropology, and colonial studies and all Canadians interested in transitional justice and human rights.
Educator Information
Contributors: Janice Cindy Gaudet, Cheryl Gaver, Robyn Green, Jula Hughes, Lawrence Martin/Wapistan, Charles R. Menzies, Arie Molena, Ronald Niezen, Simone Poliandri, and Eric Taylor Woods
Additional Information
252 pages | 6.00" x 9.00"
Synopsis:
Since the 1980s successive Canadian institutions, including the federal government and Christian churches, have attempted to grapple with the malignant legacy of residential schooling, including official apologies, the Royal Commission on Aboriginal Peoples, the Indian Residential Schools Settlement Agreement, and the Truth and Reconciliation Commission (TRC). In Residential Schools and Reconciliation, award winning author J. R. Miller tackles and explains these institutional responses to Canada’s residential school legacy. Analysing archival material and interviews with former students, politicians, bureaucrats, church officials, and the Chief Commissioner of the TRC, Miller reveals a major obstacle to achieving reconciliation – the inability of Canadians at large to overcome their flawed, overly positive understanding of their country’s history. This unique, timely, and provocative work asks Canadians to accept that the root of the problem was Canadians like them in the past who acquiesced to aggressively assimilative policies.
Excerpt
From the Conclusion:
"Canadians cannot approach reconciliation thinking that fine words and amicable gestures are enough. First Nations want their claims settled and many are interested in concluding treaties. Until Canada moves effectively to meet their desires, the country lacks the measures of social justice for Native peoples that are precondition for progress towards reconciliation...The cause of reconciliation is not hopeless; there are encouraging signs of individual and local initiatives designed to bring about reconciliation on a small scale...If enough of these small actions develop and spread, they could create the popular support for large-scale state measures that will redress the hard, material wrongs that stand in the way of reconciliation. Should that blissful day ever come, Canada will be able to advance meaningfully towards the goal of reconciliation."
Reviews
Professor Jim Miller of the University of Saskatchewan pulls back the curtain on the historical blame game. Residential Schools and Reconciliation documents Ottawa’s handling of Aboriginal issues. This is not ancient history. It just happened."
— Holly Doan, Blacklock’s Reporter. Saturday, November 18, 2017
As colonial nations around the world seek pathways to post-conflict reconciliation, J.R. Miller’s timely work is an important reminder of both the potential obstacles and the healing possibilities of such initiatives.
— Leigh Anne Williams, Publishers Weekly, February 12, 2018
Additional Information
368 pages | 6.00" x 9.00"
Synopsis:
Canada's relationship with its Indigenous people has suffered as a result of both the residential school system and the lack of understanding of the historical and current impact of those schools. Healing and repairing that relationship requires education, awareness and increased understanding of the legacy and the impacts still being felt by Survivors and their families. Guided by acclaimed Indigenous author Monique Gray Smith, readers will learn about the lives of Survivors and listen to allies who are putting the findings of the Truth and Reconciliation Commission into action.
Educator Information
Recommended for grades 4 to 8.
A teacher guide for this resource is also available: Speaking Our Truth Teacher Guide
Additional Information
160 pages | 7.50" x 9.00"
Synopsis:
This is the Final Report of Canada's Truth and Reconciliation Commission and its six-year investigation of the residential school system for Aboriginal youth and the legacy of these schools. This report, the summary volume, includes the history of residential schools, the legacy of that school system, and the full text of the Commission's 94 recommendations for action to address that legacy.
This report lays bare a part of Canada's history that until recently was little-known to most non-Aboriginal Canadians. The Commission discusses the logic of the colonization of Canada's territories, and why and how policy and practice developed to end the existence of distinct societies of Aboriginal peoples.
Using brief excerpts from the powerful testimony heard from Survivors, this report documents the residential school system which forced children into institutions where they were forbidden to speak their language, required to discard their clothing in favour of institutional wear, given inadequate food, housed in inferior and fire-prone buildings, required to work when they should have been studying, and subjected to emotional, psychological and often physical abuse. In this setting, cruel punishments were all too common, as was sexual abuse.
More than 30,000 Survivors have been compensated financially by the Government of Canada for their experiences in residential schools, but the legacy of this experience is ongoing today. This report explains the links to high rates of Aboriginal children being taken from their families, abuse of drugs and alcohol, and high rates of suicide. The report documents the drastic decline in the presence of Aboriginal languages, even as Survivors and others work to maintain their distinctive cultures, traditions, and governance.
The report offers 94 calls to action on the part of governments, churches, public institutions and non-Aboriginal Canadians as a path to meaningful reconciliation of Canada today with Aboriginal citizens. Even though the historical experience of residential schools constituted an act of cultural genocide by Canadian government authorities, the United Nation's declaration of the rights of aboriginal peoples and the specific recommendations of the Commission offer a path to move from apology for these events to true reconciliation that can be embraced by all Canadians.
Synopsis:
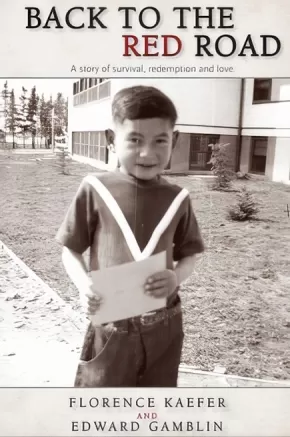
In June 1967, Norway House Indian Residential School of Manitoba closed its doors after a somewhat questionable past. In 1954, when Florence Kaefer was just nineteen, she accepted a job as a teacher at Norway House. Unaware of the difficult conditions the students were enduring, Florence and her fellow teachers nurtured a school full of lonely and homesick young children. After a few years, Florence moved to Vancouver Island with her new husband where she continued to teach, thinking often of the children of Norway House.
Many years later, after the death of her husband, Florence unexpectedly reconnected with one of her Norway House students, Edward Gamblin. Edward had been only five when he was brought to Norway House and Florence remembered him as a shy and polite young boy. Leaving the school at sixteen, Edward faced some challenges in a world that was both hostile and unfamiliar to him. But Edward found success and solace in his career as a musician, writing songs about the many political issues facing Aboriginal people in Canada. On a trip to Manitoba, Florence discovered Edward's music. She was captivated by his voice, but shocked to hear him singing about the abuse he and the other children had been subjected to at Norway House.
Motivated to apologize on behalf of the school and her colleagues, Florence contacted Edward. "Yes, I remember you and I accept your apology," Edward told her. "Reconciliation will not be one grand, finite act. It will be a multitude of small acts and gestures played out between individuals." The story of their personal reconciliation is both heartfelt and heartbreaking as Edward begins to share his painful truths with his family, Florence and the media. Three years after Edward's death in in 2010, Florence has continued to advocate for truth and reconciliation. BACK TO THE RED ROAD is more than one man's story: it is the story of our nation and how healing can begin, one friendship, one apology at a time.
Additional Information
|